
It’s the reason double-entry accounting works, and it’s the starting point for every financial statement your clients or stakeholders depend on. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business. In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as owner’s equity. Paying off a loan reduces both assets (cash) and liabilities (loans payable) by an equal amount, maintaining the equation’s equilibrium. When an owner withdraws cash for personal use, assets (cash) decrease, and equity (owner’s withdrawals) decreases proportionally.
ROE EXERCISE: MANAGEMENT OF WORKING CAPITAL AND RECEIVABLES AND RETURN ON EQUITY
There are mainly 3 affecting components of the accounting equation, with numerous influential variables. These variables can create changes in the numbers, but the equation will still be balanced. This is the equation that forms a double-entry connection for how is sales tax calculated all accounting entries in businesses, i.e., every entry has a debit as well as a credit side.

BONDS PAYABLE
Because the balance sheet is a real-world snapshot of this formula in action. Assets are listed on one side, while liabilities and equity make up the other, and both sides must always match. Every asset, liability, and equity account you manage ties back to this equation.

Key Components in Accounting Equation
- Some assets are less liquid than others, making them harder to convert to cash.
- The Balance Sheet is a detailed representation of the accounting equation at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of a company’s financial health.
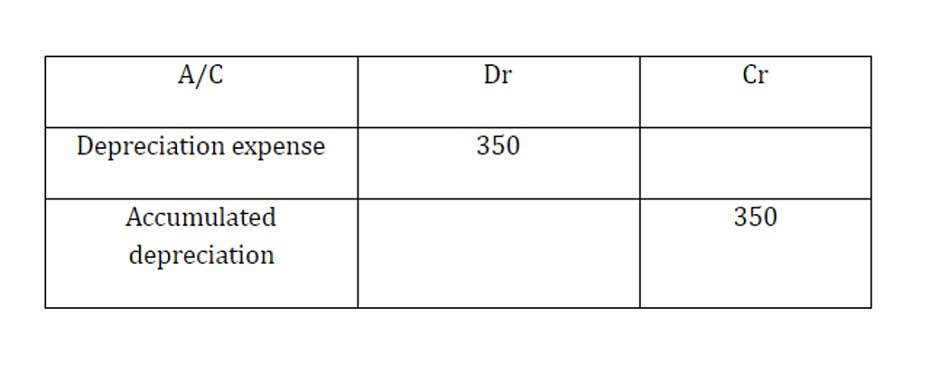
- For example, purchasing inventory with cash increases one asset (inventory) while decreasing another (cash), with no effect on the equation’s total.
- The balance sheet is organised with assets listed on one side and liabilities and equity on the other.
- The balance sheet serves as a tangible manifestation of this accounting principle, confirming that the company’s financial records are in balance.
We will examine the operations of “ABC Enterprise” to show how to analyze transactions in terms of the accounting equation. The company must analyze each event to determine whether or not it has an effect on the variables that make up the accounting equation. The transaction that takes place as a result of an event can bring about any of the following changes to the components of the accounting equation. Typically, an increase in revenues will result in an increase in the value of an owner’s equity.
The accounting equation represents the relationship between a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. In the expanded version, revenue increases equity, while expenses and dividends reduce it. In essence, the accounting equation shows that a company’s total assets are financed by either borrowing money (liabilities) or taking in money from owners (equity). The equation must always balance out, underlining the concept of the double-entry bookkeeping system – every debit must have a corresponding credit, and vice versa. This transaction increases an asset (equipment) while simultaneously decreasing another asset (cash).
- This expanded equation is crucial for corporations as it allows a deeper analysis of financial results, showing how operations impact shareholder equity and profitability.
- Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program.
- For instance, high liabilities might signify potential solvency issues despite a mathematically balanced equation.
- Whether your business is establishing basic bookkeeping processes or refining sophisticated financial reporting, the accounting equation remains your fundamental reference point.
- Required Explain how each of the above transactions impact the accounting equation and illustrate the cumulative effect that they have.
- The fundamental accounting equation is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system, providing a structured framework for recording and summarizing a business’s financial activities.
- It is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping system of accounting, which helps us understand from the illustration above that total assets should be equal to total liabilities.
What are Specific Names for Equity on the Balance Sheet?
The accounting equation is ingeniously designed to always fundamental accounting equation remain balanced, meaning the total amount of assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and equity. For instance, when a company takes out a loan, assets (cash) increase, as do liabilities (loans payable), which keeps the equation balanced. Similarly, when a business issues new shares, both assets (cash) and equity increase.
- We will examine the operations of “ABC Enterprise” to show how to analyze transactions in terms of the accounting equation.
- Conversely, equity decreases with owner withdrawals or dividends, and expenses.
- Owners can increase their ownership share by contributing money to the company or decrease equity by withdrawing company funds.
- Since the owner is also alien to business and the owner’s contribution is to be treated as a liability we can say that total liabilities is equal to total capital.
- Here’s a screenshot of Alphabet Inc.’s Consolidated Balance Sheets from its 10-K annual report filing with the SEC for the year ended December 31, 2021.
The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. Since equity and liabilities are related, gym bookkeeping any changes in revenue or expenses affect the overall financial position of a company. This insight is crucial for accurate reporting and strategic planning.
